Why Modern Django Outperforms Older Versions in Web Development Why Modern Django Matters Over the past two decades, Django Web Development has evolved from a niche Python tool to one of the most reliable and scalable frameworks for building web applications. Originally open‑sourced in 2005, Django’s early releases focused on solving practical, newsroom‑driven problems: rapid content updates, reusable components, and straightforward database interaction. Today, it’s used by companies such as Instagram, Pinterest, Mozilla and others, which speaks to its maturity and adaptability. The framework’s philosophy hasn’t shifted dramatically since its inception. It still emphasizes clean code, security by default and a comprehensive set of built‑in tools that let developers focus on business logic rather than boilerplate. What has changed is how the framework embraces newer patterns, performance improvements and scalability demands that older versions simply weren’t built to address. What Older Versions Offered In the early days of Django, releases such as 1.0 and 1.2 laid the groundwork for what the framework would become. Django 1.0 was the first stable version that dropped the “beta” tag after years of development. It introduced a revamped admin interface, improved template escaping, better Unicode support and a foundational file storage system. This era was defined by two priorities: Making web development fast. Django was one of the first frameworks to include so much out of the box, reducing the need for developers to add plugins for basic capabilities like authentication, ORM and admin panels. Improving security and stability. Even early versions included protection against common vulnerabilities, a practice that remains core to the framework today. While these releases were ground breaking for their time, they had limitations. Performance optimization was basic compared to what modern platforms demand. Asynchronous tasks, native async support and other modern web patterns were not part of the core. The community filled many gaps with third‑party packages, but relying on external tools often made projects harder to maintain. What Modern Django Brings to the Table Fast forward to the Django of today. The framework continues to evolve while keeping its core values intact. Recent versions include enhanced asynchronous handling, modern ORM improvements and refined tools that support large, traffic‑heavy applications. According to community reports, newer releases are pushing deeper async capabilities, improved form rendering and a more efficient database query system that weren’t possible in older versions. From a customer perspective, the benefits are clear: 1. Improved performance and scalability Modern Django can handle more complex workloads while minimizing response times. Developers now get better async support out of the box, making apps more responsive and capable of handling concurrent operations without blocking. 2. Consistent security updates One of Django’s strengths has always been its security focus. While older versions had basic defenses against threats like SQL injection and CSRF, newer releases keep pace with emerging vulnerabilities. Security patches and fixes are regularly released, ensuring long‑term support and trust. 3. Cleaner development experience The “batteries‑included” philosophy remains, but tools have become more polished. From a more intuitive ORM to improved error reporting and debugging features, modern Django strips away much of the frustration developers once faced. This translates to faster iteration cycles and better code quality for customers. 4. Ecosystem maturity Older versions relied heavily on third‑party tools for features like timers, task queues and advanced caching. Today those integrations are more stable and better documented. Some capabilities, such as asynchronous views and modern form handling, are now supported by Django’s core without needing external dependencies. Why Upgrading Matters for Your Business If you’re building or maintaining a web application, sticking with older Django versions can hold you back. Here’s why: Security: Older releases eventually reach end of life and stop receiving patches. This exposes your application to risk and compliance issues. Performance: Modern user expectations demand speed. Improvements in async handling, database efficiency and caching can reduce load times and keep users engaged. Developer Productivity: Teams familiar with the latest Django features can deliver new modules faster, with less technical debt. This affects project timelines and total cost of ownership. Future‑proofing: The web is constantly changing. Staying current with Django versions means smoother transitions to emerging frontend frameworks, APIs, DevOps practices and cloud deployments. In contrast, older versions were limited in handling modern demands. They required workarounds for async tasks, didn’t optimize for high concurrency and lacked many of the built‑in efficiencies developers take for granted now. These differences become more apparent in complex apps or in those expected to scale quickly. Balancing Legacy with Innovation Some teams still run older Django versions for legacy reasons. Migration can be nontrivial, especially in large codebases with custom middleware or tightly‑coupled modules. The key is to evaluate both technical debt and future needs. Planning upgrades incrementally, reviewing release notes and refactoring code incrementally can make the transition smoother. Conclusion Across its lifespan, Django Web Development has grown from a solid but simple framework to a robust, scalable engine powering modern web applications. While older versions were remarkable for their time and shaped how web development evolved, current releases bring meaningful enhancements in performance, security and developer productivity. For businesses that care about reliability, maintainability and future growth, choosing modern Django is not just a technical decision, it’s a strategic investment in long‑term success. Django Web Development remains a compelling option for any web project.
Category: Blog
Blog
Why Modern Flask Web Application Development Still Outperforms Older Versions
Why Modern Flask Web Application Development Still Outperforms Older Versions In the world of Python web frameworks, Flask Web Application Development has carved out a distinct space for developers who want simplicity without sacrificing power. Over the years, Flask has matured significantly. While early versions laid the foundation for lightweight web apps, modern releases have refined that foundation with performance improvements, better tooling, and stronger community support. Analysing Flask’s evolution and why teams choose it today helps anyone deciding on the best framework for their next project. This article looks at how Flask has improved over its older versions, what sets it apart from alternatives, and what those improvements mean in practical terms. The Core Philosophy Then and Now Flask began as a simple microframework built around the idea of giving developers freedom. Its early versions focused on minimalism: just enough to get a web app running, with the expectation that developers would add what they needed. At that time, Flask Web Application Development meant wiring up routes, templates, and database connections from scratch. This flexibility was a double‑edged sword. On one hand, it made learning Flask approachable. On the other hand, it left out useful conventions and tooling that could speed up development. Modern Flask still horons that philosophy but with more structure and built‑in support for common tasks. For example, configuration patterns, blueprint systems for modular apps, and support for asynchronous workflows are now part of Flask’s core direction. These improvements reduce boilerplate and make applications easier to maintain. What Has Changed Since Older Flask Versions 1. Better Routing and Request Handling Early Flask routing was simple and adequate for basic apps. Modern versions have optimized routing performance and added more flexible parameter handling. Developers can now define rules for route converters that were harder to implement previously. This makes it easier to manage URLs in large applications. Request handling has seen parallel improvements. Modern Flask integrates better with Python’s async features, allowing parts of the application to perform non‑blocking I/O. Older versions were strictly synchronous, which limited performance in high‑load or real‑time use cases. 2. Blueprint System for Larger Apps In early releases, developers often ended up with a single large application file. As projects grew, this became harder to manage. Flask introduced blueprints to allow modular application structure. Blueprints let developers group routes, templates, and static files logically. This pattern encourages cleaner code organization and team collaboration. This modular approach contrasts sharply with pre‑blueprint development, where structure had to be invented on the fly. 3. Enhanced Extensions and Ecosystem Flask’s extension ecosystem has always been one of its strengths. Extensions provide database integration, authentication, RESTful APIs, and more. While older versions supported these via third‑party addons, modern Flask makes extension integration smoother and more consistent. For example, Flask‑SQL Alchemy and Flask‑Login are now stable, widely adopted tools. They work with minimal configuration and follow common patterns that teams can pick up quickly. This ecosystem maturity reduces development risk and time‑to‑value for projects. 4. Configuration and Environment Management Early Flask apps often placed configuration settings directly in application scripts. This worked for simple cases but didn’t scale. Today’s Flask encourages the Twelve‑Factor App methodology, promoting environment‑based configuration. This helps teams manage settings across development, staging, and production without code changes. This change, subtle as it may seem, significantly improves deploy ability and stability. Performance and Scalability Advances Performance isn’t just about raw request throughput. It also includes startup speed, memory usage, and responsiveness under load. Modern Flask optimizes these areas without adding unwanted complexity. With support for async views and integration with ASGI via adapters like Quart, Flask can now play in spaces traditionally dominated by more monolithic frameworks. Older versions simply didn’t have this capability. For high‑traffic applications, developers can pair Flask with production‑grade servers like Guni corn or Unicorn. The combination provides a robust deployment path that retains Flask’s simplicity but adds safety and scalability. Developer Experience Improvements Developer experience has grown from nice‑to‑have to a major decision factor. Modern Flask tooling includes: Better debugging tools Integrated CLI for common tasks More descriptive error messages Official documentation with clear examples In contrast, early Flask documentation was shorter and less comprehensive. While it got developers started, it didn’t always guide them beyond the basics. Today’s documentation and examples make learning and adopting best practices much easier. This matters especially for teams onboarding new members or scaling existing ones. A clear, shared understanding of conventions accelerates progress and reduces friction. Why Teams Choose Flask Today There’s no shortage of Python web frameworks. Yet, many teams pick Flask for reasons that reflect its ongoing improvements: Flexibility without compromise: Developers get control over architecture without being forced into patterns they don’t need. Rich ecosystem: Mature extensions handle common challenges like authentication and database management. Clear upgrade paths: Recent versions address issues that developers grappled with in older releases. Strong community support: Active contributors ensure bugs are fixed, features are added, and documentation stays relevant. All these benefits feed into a positive developer experience and reliable production performance. When Flask Might Not Be the Best Fit Flask isn’t always the right choice. For example, if your project demands tightly integrated admin interfaces, built‑in object models, or convention‑first tools like Django, Flask might require more initial setup. That said, the enhancements in recent versions reduce these gaps by supporting extensions that fill those needs without bloating the core framework. Final Thoughts Choosing the right tool means understanding both its history and its present capabilities. Modern Flask Web Application Development reflects years of refinement and community feedback. Compared to its older versions, Flask today offers better structure, improved performance, and a more complete developer experience. In conclusion, for teams that want a clear, flexible path from prototype to production, Flask Web Application Development remains… Continue reading Why Modern Flask Web Application Development Still Outperforms Older Versions
The Shift From Traditional Marketing to Digital Marketing: Why Modern Tools Deliver Better Results
The Shift From Traditional Marketing to Digital Marketing: Why Modern Tools Deliver Better Results For years, businesses relied on print ads, billboards, radio spots, and door-to-door promotions to reach customers. These methods worked when audiences were less fragmented and had limited media choices. Today, attention spans have changed, and customers expect brands to communicate quickly, consistently, and with relevance. This shift has made digital marketing not just helpful but essential. What’s driving this transformation is the growing adoption of advanced platforms like Digital Marketing Automation Software , which brings speed, accuracy, and personalization that older marketing models simply cannot match. Traditional Marketing: Effective Once, Limited Now Older marketing methods had a predictable rhythm. A business would design a print ad, approve artwork, negotiate newspaper placements, and wait days or weeks for the audience to respond. Tracking performance was slow and mostly based on guesswork. Customer engagement lacked personalization, and feedback loops were inefficient. These methods also required hefty budgets. A small business often struggled to compete with brands that could afford recurring print ads or large hoardings. Even when campaigns performed well, the lack of real-time data made optimization difficult. Today’s market demands agility. Customers expect instant responses, tailored content, and cross-platform consistency. This is where modern digital tools outperform traditional models in every key metric. Digital Marketing: Built for Speed, Precision, and Scale Digital marketing reshaped customer engagement by offering measurable, targeted, and time-sensitive interactions. Instead of waiting for customers to discover an ad, businesses can now reach them based on behavior, demographics, interests, device type, or even purchase intent. Real-time dashboards help teams track clicks, conversions, and revenue as they happen. Tools such as Digital Marketing Automation Software bring order to this ecosystem by automating campaigns, segmenting audiences, and ensuring consistent brand communication across multiple touchpoints. Why Digital Marketing Outperforms Older Methods 1. Better Targeting and Customer Understanding Traditional marketing relied on broad messaging. A newspaper ad reached a wide audience, but only a small percentage fit the intended customer profile. Digital platforms allow businesses to identify ideal customers through data points such as search behavior, past purchases, browsing interests, and engagement history. This gives brands the ability to deliver messages that matter. 2. Real-Time Performance Tracking Unlike traditional campaigns where results took weeks, digital campaigns offer immediate insights. Click-through rates, conversions, customer journeys, and drop-off points can be tracked live. This helps marketers adjust campaigns instantly if something isn’t working. 3. Lower Costs with Higher Conversion Potential Old methods required large budgets for design, printing, and placements. Digital campaigns can start with small budgets and scale based on results. Even the smallest business can run highly targeted ads on social media or search platforms. 4. Automated Processes Save Time and Reduce Errors Modern businesses often run campaigns across email, social media, websites, messaging apps, and ad networks. Doing this manually can overwhelm any team. Tools like Digital Marketing Automation Software centralize these tasks, automate repetitive activities, and minimize manual errors. 5.Personalized Customer Experiences Today’s customers expect brands to remember their preferences. Digital tools help businesses design personalized journeys based on past actions. For example, someone who browses a product but doesn’t purchase can automatically receive a reminder email or tailored offer. 6. Faster Customer Engagement Digital platforms allow immediate response through chatbots, automated emails, instant notifications, and real-time support. This speed matters because customers often choose brands that respond fastest. How Automation Makes Digital Marketing Even More Effective Digital marketing was already powerful, but automation has taken it to the next level. Automation ensures every lead receives timely communication, every segment gets the right content, and every campaign runs without manual monitoring. Here’s how automation enhances performance: Lead Nurturing: Automated sequences guide prospects through the sales funnel with relevant content. Campaign Scheduling: Businesses can plan campaigns days or months ahead and let the tool execute them. Segmentation: Users are grouped based on behavior, demographics, or interests for more precise targeting. Consistency: Automation ensures messaging stays on track across multiple channels and time zones. Scalability: Whether handling 1,000 or 1,000,000 users, automation keeps processes smooth without extra manpower. This combination of efficiency and personalization helps businesses deliver experiences that older marketing strategies simply could not match. Customer-Centric Benefits Driving Modern Growth Digital transformation is not only about better technology. It’s about customer satisfaction. Modern tools help brands understand customer needs, communicate clearly, and deliver value at the right moment. Key customer-centric advantages include: Simplified service experience Faster query resolution Personalized recommendations Convenient digital interactions Transparent tracking of orders or services Better engagement through tailored content These improvements help brands build trust. When customers feel understood, they stay longer and recommend the business to others. Why Businesses Must Move Beyond Traditional Marketing Old marketing models served their time well. But today’s customers expect speed, transparency, and personalized attention. Competing in an environment where digital experiences define brand perception requires modern systems that can adapt quickly. Businesses that continue relying on outdated methods risk losing relevance and visibility. Digital transformation is no longer optional. It is necessary for brands that want to grow in a competitive market. Conclusion The evolution from traditional marketing to modern digital strategies has created new opportunities for businesses to connect meaningfully with their customers. Adopting platforms like the Digital Marketing Automation Software helps companies streamline operations, deliver personalized experiences, and respond to market changes with confidence. The future belongs to businesses that embrace technology and prioritize customer engagement at every step.
An Analytical Look at the Advantages of Digital Marketing Over Older Methods
An Analytical Look at the Advantages of Digital Marketing Over Older Methods Businesses today operate in an environment where customer behaviour shifts quickly, competition grows every day and buying decisions often begin online. Older marketing methods like print ads, billboards, radio spots and door-to-door promotions once played a central role, but they no longer offer the speed or precision needed to reach modern audiences. This shift has made digital tools essential for every brand looking to grow. Among these tools, the Online Marketing Application has become a powerful engine for customer outreach, engagement and performance measurement. Why Digital Marketing Has Become the Core of Modern Growth Traditional marketing depends heavily on broad messaging and large budgets. While it can create visibility, it lacks the ability to track user behaviour, personalize messaging or adjust campaigns in real time. Today’s customers expect more. They research online, compare options across devices and engage with brands on social platforms before making a decision. Digital marketing meets these expectations by offering direct access to customers, better targeting precision and measurable results. Businesses now want agility. They want to respond fast, understand what works and avoid unnecessary spending. With tools like analytics dashboards, automation platforms and customer segmentation modules, digital marketing provides flexibility that older methods cannot match. This is why many companies adopt the Online Marketing Application to manage campaigns efficiently and improve return on investment. Better Targeting and Audience Precision A key advantage of digital marketing is the ability to reach the right audience at the right time. Traditional methods cast a wide net, hoping to capture attention. Digital channels, on the other hand, allow businesses to focus on specific customer groups based on age, location, interest, online activity and even purchase behaviour. This improves campaign efficiency and reduces wasted spending. Marketers can set custom parameters, track which ads are performing well and work with data instead of assumptions. Whether it’s social media ads, email campaigns or search engine marketing, the accuracy of digital tools makes customer outreach more effective and less expensive. Real-Time Insights and Measurable Performance Older marketing methods provide limited feedback. Once a flyer is printed or a billboard is installed, it’s difficult to measure how many people saw it or whether it influenced their decisions. Digital marketing solves this problem by offering complete visibility into user activity. Tools such as website analytics, ad dashboards and automated reporting give instant access to metrics like impressions, click-through rates, conversions and customer journeys. Businesses can see what works, what doesn’t and adjust campaigns without delay. This real-time optimization helps improve performance, reduce costs and build a more reliable marketing strategy. Stronger Customer Engagement Digital platforms make it easier for businesses to communicate with customers. Social media, email newsletters, chatbots, mobile apps and targeted content help brands stay connected and build long-term trust. Traditional media is mostly one-way communication. Today’s digital channels allow customers to respond, ask questions, share feedback and interact with brands whenever they want. This two-way engagement creates stronger relationships and helps businesses understand customer expectations more clearly. Companies using the Online Marketing Application can automate responses, personalize communication and manage customer journeys across multiple touchpoints. This makes the overall experience smoother and more aligned with customer expectations. Higher Flexibility and Faster Adaptation Digital tools allow businesses to modify campaigns instantly. If an ad is underperforming, it can be changed within minutes. If customer behaviour shifts, targeting criteria can be adjusted. Traditional campaigns lack this flexibility because printed materials or broadcast slots cannot be changed after they are released. The speed of digital marketing helps companies stay relevant, adapt to trends and respond to competitor movements without losing time or budget. Lower Cost and Higher ROI Older marketing methods often demand high upfront investments. Printing, outdoor advertising and mass media promotions can be expensive and difficult to measure. Digital marketing allows businesses to start with small budgets, test campaigns and scale only what works. Pay-per-click, email marketing, content marketing and social promotions offer cost-friendly options for businesses of all sizes. Because performance is measurable, budgeting becomes easier and more strategic. Over time, this leads to better returns and consistent growth. Personalized Experiences for Modern Customers Personalization is one of the strongest advantages of digital marketing. Customers today expect relevant content, custom offers and communication that fits their needs. Digital platforms collect behaviour data, which helps brands create personalized recommendations and targeted campaigns. Older methods treat every customer the same. Digital tools treat each customer individually. This difference drives higher engagement, stronger conversions and better customer loyalty. Scalable and Future-Ready Digital marketing solutions are built to grow with the business. As companies expand products, services or target markets, the same platforms can handle larger audiences and more complex campaigns. Older marketing methods require bigger budgets and more manual coordination as the business grows. Automation, AI-driven insights and integrated marketing tools make scaling smoother, faster and more efficient. This is one of the main reasons businesses are transitioning from traditional media to digital-first strategies. Conclusion Digital marketing offers accuracy, flexibility and measurable performance that older methods simply cannot match. It supports stronger customer relationships, reduces unnecessary spending and gives businesses the tools they need to grow in a fast-changing market. For companies aiming to stay competitive and customer-focused, adopting an Online Marketing Application provides a clear advantage and a smarter way forward.
An Analytical Look at How Digital Marketing Outperforms Older Methods
An Analytical Look at How Digital Marketing Outperforms Older Methods Marketing has changed more in the last decade than in the previous fifty years. Traditional methods like print ads, billboards, radio and in-person promotions once shaped how businesses reached customers. These channels still hold value, but they lack the precision, speed and scalability modern brands need. Today, the real competitive edge comes from digital ecosystems that offer targeted outreach, measurable performance and real-time engagement. A Web-Based Marketing Platform plays a central role in this shift by helping businesses connect with audiences more effectively. The Limitations of Older Marketing Approaches Older marketing strategies relied heavily on broad messaging. Businesses would distribute flyers, run newspaper ads or invest in outdoor hoardings and hope the right people noticed. While this approach created visibility, it rarely offered insights. There was no direct way to track engagement, measure conversions or understand customer behavior. Budget inefficiency was another challenge. Brands often spent large amounts without knowing which campaigns worked. Adjusting a strategy meant waiting weeks, and results were mostly based on assumptions. These limitations made it hard for small and mid-sized businesses to compete with companies that had large advertising budgets. Digital channels removed these barriers. They gave businesses control, speed and precision that older methods could never deliver. Why Digital Marketing Delivers Better Outcomes Digital marketing offers several advantages that explain why it outperforms older versions. The ability to reach specific audiences, track real-time performance and adjust campaigns instantly makes digital channels more reliable and cost-effective. With analytics tools, businesses understand how visitors interact with content. They can identify what works, pause campaigns that underperform and scale the ones producing strong results. This creates a cycle of continuous improvement. Modern platforms also support omnichannel engagement, where customers interact across websites, social media, email, search engines and mobile apps. A Web-Based Marketing Platform helps unify these interactions so brands stay connected with customers at every stage of the buying journey. The Role of Real-Time Insights Real-time data is one of the biggest strengths of digital marketing. Businesses can monitor impressions, clicks, leads and purchases as they happen. This level of transparency is unmatched in traditional media. Instant reporting helps brands react to market trends faster. If a particular product gains traction, campaigns can be adjusted on the same day. If customer behavior changes, messaging can shift immediately. This agility protects budgets and improves outcomes. Older methods cannot support this flexibility. Once a print ad is published or a billboard is installed, changes are expensive and slow. Personalization and Customer Experience Digital marketing makes personalization possible. Brands can segment audiences by interests, location, buying history and behavior. This ensures the message aligns with what the customer actually wants. Tailored content builds trust, increases engagement and improves conversion rates. A web-enabled platform strengthens this experience by capturing customer data across channels and delivering the right message at the right time. Traditional methods offer little opportunity for personalization. Every customer receives the same message, whether or not it fits their needs. Cost Efficiency and Higher ROI Digital channels offer more control over spending. Businesses can start with a small budget, test campaigns and scale only when performance is proven. Detailed cost breakdowns help brands understand exactly where their money goes. With older marketing, spending is fixed upfront. There is no guaranteed return and no way to optimize based on performance. A Web-Based Marketing Platform makes the investment even more cost-effective by centralizing campaign management, eliminating manual tasks and improving workflow efficiency. Building Long-Term Customer Relationships Digital marketing is not just about promotion; it is also about relationship building. Customers engage through comments, chats, email responses and social interactions. This two-way communication builds loyalty and helps brands understand expectations more clearly. Older methods do not create this level of interaction. Communication stays one-sided, and customers have limited ways to respond. Digital ecosystems nurture long-term relationships through: Automated email sequences Retargeting campaigns Loyalty programs Consistent content delivery User behavior tracking These tools ensure customers stay connected throughout their journey. Scalability for Growing Businesses Digital platforms grow with the company. Whether a business expands to new markets or launches new products, campaigns can be scaled with minimal effort. New audiences can be reached through online ads, SEO strategies, influencer partnerships or targeted content. Older methods require larger budgets and more physical resources for expansion, making scaling expensive and slow. A modern marketing platform ensures businesses remain flexible as they grow, without adding operational burdens. Enhanced Reliability Through Automation Automation helps brands save time, reduce errors and maintain consistency. Tasks such as scheduling posts, sending emails or updating customer segments can run on autopilot. This creates a smooth workflow and ensures customers receive timely communication. Automation was not possible with older marketing approaches. Everything depended on manual effort, which increased costs and slowed down delivery. Conclusion Digital marketing has transformed how businesses attract, engage and retain customers. It offers speed, accuracy, affordability and measurable outcomes that older strategies cannot match. For companies aiming to stay competitive and customer-focused, adopting a Web-Based Marketing Platform brings the structure, insight and flexibility needed to succeed in a fast-changing market.
Why Modern Python Outperforms Older Versions for Today’s Enterprise Needs
Why Modern Python Outperforms Older Versions for Today’s Applications Technology evolves fast, and programming languages need to keep up with rising performance demands, security expectations and business goals. Python has seen major transformations in recent years, especially with the growth of Python 3.x and continuous improvements in speed, memory handling and security. Compared to older versions, modern Python offers real advantages for teams building scalable applications, data platforms and intelligent automation. For companies aiming to deliver dependable digital services, the shift to newer Python releases brings clear, measurable benefits. One of the biggest shifts in Python’s evolution is its improved architecture. Earlier versions were slower, relied heavily on outdated libraries and lacked the performance boosts required for large-scale computing. Today, enhanced interpreters like CPython 3.12 and upcoming just-in-time compilation capabilities help applications run faster with fewer system resources. This difference becomes crucial when companies rely on Python for analytics, automation or customer-facing platforms where response time matters. Security gaps were also more common in older versions. Many outdated Python libraries are no longer maintained, leaving applications open to vulnerabilities and compliance risks. Modern Python releases receive regular security patches, follow stronger encryption standards and support more reliable dependency management. Businesses handling sensitive data cannot afford outdated frameworks, especially when customers expect safe digital experiences. Updated Python environments offer a more secure foundation without the hidden threats that come with legacy systems. Another major improvement is library support. Older versions restricted developers to limited tools and slow integrations. Today, Python’s modern ecosystem includes powerful frameworks for artificial intelligence, automation, API development and cloud deployment. Tools like FastAPI, Django, Pandas, TensorFlow and SQLAlchemy perform optimally only on current Python versions. This helps development teams innovate faster and deliver better digital products without forcing long workarounds or patch fixes. This efficiency directly benefits companies using Python for Enterprise Applications to support their operations. When businesses adopt current Python versions, they gain faster processing, smoother integrations and reduced downtime. Modern frameworks also help them respond to customer needs quicker by supporting microservices, real-time analytics and scalable workloads. These capabilities were difficult or slow to implement on older versions. Performance tuning is another area where newer Python releases stand out. Features like improved garbage collection, asynchronous processing and optimized syntax enable teams to build applications that handle more users at once. For companies managing large customer bases or heavy transaction volumes, this scalability becomes essential. Modern Python allows applications to grow without requiring complete system redesigns, reducing long-term costs and complexity. Developer productivity has also improved. Newer versions introduce cleaner syntax, better error messages and enhanced debugging tools. This helps teams reduce development time and avoid common mistakes that were harder to identify in older Python. Faster development cycles mean companies can bring digital services to market sooner, keep up with competition and continuously update features based on customer feedback. The shift to cloud computing further highlights the value of current Python environments. Cloud-native architectures rely on containerization, orchestration and API-driven workflows. Modern Python aligns well with these technologies, offering seamless performance in Docker, Kubernetes and serverless environments. Older Python versions often struggle with compatibility, slower service spin-up and unpredictable performance across distributed systems. For companies depending on cloud-based Python for Enterprise Applications, this compatibility becomes a strategic advantage. Customer expectations are also driving this shift. Today’s users expect frictionless digital experiences, fast load times and accurate results across applications. Whether a company manages portals, dashboards, automation tools or analytics engines, modern Python supports smoother interactions and more stable performance. Legacy performance lags can affect customer trust, especially in platforms tied to finance, healthcare or e-commerce. Updated Python environments ensure reliability even when usage surges. Another reason modern Python outperforms older versions is its strong community support. Developers now benefit from active forums, documentation, continuous updates and quick resolutions to known issues. Older Python branches receive little or no support, which increases maintenance cost and risk. With updated versions, companies can rely on stable releases, predictable updates and better long-term planning for their digital systems. Integration flexibility has also expanded. Modern Python works well with API gateways, AI engines, message queues, microservices and cloud databases. This helps companies create connected ecosystems without friction. Older Python versions lacked the structure and performance required for seamless integrations, resulting in more manual work and slower system communication. With improved compatibility, teams can develop unified platforms that handle workflows from end to end. Financial efficiency is another overlooked benefit. Maintaining old Python systems requires more manual fixes, security patching and specialized developers familiar with outdated code. This increases costs over time. Upgrading to modern Python reduces operational burden, simplifies hiring and allows teams to focus on building rather than fixing. When companies invest in updated environments, they can redirect their resources toward innovation and customer experience. A modern digital strategy requires performance, security and scalability. Python’s evolution ensures businesses can deliver these qualities without compromise. With improved computing efficiency, stronger integration capabilities and a growing set of modern libraries, Python continues to be the foundation for intelligent, customer-focused applications. Older versions simply cannot keep up with today’s speed, complexity and user expectations. Conclusion For companies building robust platforms and digital products, upgrading to modern Python delivers higher performance, stronger security and long-term stability. By aligning with current tools and best practices, organizations that depend on Python for Enterprise Applications can serve customers faster, reduce risks and stay prepared for future technological change.
The Advantages of Using Node.js for Modern Digital Platforms
The Advantages of Using Node.js for Modern Digital Platforms Node.js has become one of the most influential technologies in the software world. Its rise is closely linked to the growing demand for scalable, real-time digital experiences. Businesses today expect fast delivery, efficient performance, and the ability to adapt quickly. That is why Node.js has become a preferred platform for teams building modern applications. It offers a blend of speed, flexibility, and simplicity that aligns well with the evolving needs of companies investing in Web Development. Node.js is built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, which allows developers to use JavaScript on both the front end and back end. This eliminates the silos that often slow down projects and helps teams streamline their workflow. Most importantly, Node.js is designed for performance. It handles large volumes of requests, supports real-time updates, and offers tools that help businesses launch products faster. Why Node.js Matters Today Digital products are no longer simple. They involve live dashboards, instant notifications, connected devices, and fast API integration. Tools that rely on slow, traditional request-response cycles struggle in this environment. Node.js solves this by using non-blocking I/O and event-driven architecture, which makes it ideal for applications that need constant updates. This is especially important for organizations that rely on interactive customer platforms. Whether you’re running a marketplace, an analytics tool, a booking system, or a streaming platform, Node.js helps your product stay responsive even during heavy traffic. Many global companies have adopted it for this reason. The Key Advantages of Using Node.js 1. Faster Development Cycles Node.js speeds up the development process by using a single language across the entire stack. This reduces context switching and allows teams to collaborate more efficiently. Teams can reuse code between the client and server, which lowers development time and improves consistency across features. 2. Superior Performance and Scalability Performance has always been a core strength of Node.js. It can manage thousands of concurrent connections without slowing down. Its event-driven model is built to scale, making it ideal for businesses expecting rapid growth. This matters most for applications that depend on real-time interaction, such as chat services, gaming platforms, and logistics dashboards. 3. Rich Ecosystem and Community Support The NPM ecosystem provides a massive library of modules that speed up development. Instead of building every function from scratch, teams can integrate tested packages to reduce time and cost. This ecosystem grows every year, making Node.js even more attractive for Web Development projects that need reliable and modern tools. 4. Real-Time Data Handling Node.js is built for real-time use cases. Whether you are tracking live user analytics, updating stock availability, or running instant messaging features, its architecture makes these tasks efficient. Customers today expect immediate responses and smooth interaction. Node.js helps companies meet that expectation without sacrificing reliability. 5. Cost Efficiency Using the same language across the stack can lower overall development costs. You don’t need separate backend and frontend specialists for every task. Teams can adapt more easily, and hiring becomes simpler. Node.js also reduces the servers needed to manage traffic, especially when handling numerous live connections. 6. Cross-Platform Flexibility Node.js supports the creation of desktop, mobile, and server applications through different frameworks. This gives businesses the freedom to expand their digital ecosystem without switching technologies. With the right setup, you can reuse core logic across platforms while keeping the user experience consistent. 7. Improved Developer Productivity Node.js gives developers access to modern tools, automation options, and fast testing workflows. This leads to fewer bottlenecks and quicker delivery cycles. For companies that prioritize speed, this productivity boost can have a direct impact on revenue and customer satisfaction. How Node.js Enhances Customer Experience Technology choices don’t just affect development teams. They also influence how customers interact with your product. Node.js helps businesses deliver faster load times, fewer errors, and seamless real-time features. A responsive platform builds trust, encourages users to stay longer, and makes digital interactions more enjoyable. Node.js also supports microservices architecture, which helps companies release updates without downtime. This means you can introduce new features, fix bugs, and scale smoothly without interrupting the user experience. For growing companies, this flexibility is a major advantage. Business Use Cases Where Node.js Excels Node.js works well in industries that prioritize speed and data-driven functionality. Typical use cases include: Real-time tracking systems E-commerce platforms Streaming services Collaboration tools On-demand apps IoT and automation analytics Customer dashboards and reporting tools Each of these applications requires a mix of fast performance, real-time updates, and scalable architecture. Node.js handles all three effectively, which explains its adoption across sectors. Conclusion Node.js offers a strong blend of speed, flexibility, and scalability that helps businesses deliver better digital experiences. Its architecture supports real-time functionality, reduces development cycles, and helps teams operate more efficiently. Companies that want to stay competitive in Web Development can rely on Node.js to power modern, customer-focused applications that perform well at scale.
Do You Know the Magic of Angular 19 over the old versions
Do You Know the Magic of Angular 19 over the old versions The web ecosystem moves fast, and customers expect smooth, secure and modern digital experiences. This is where Angular 19 steps forward with a remarkable upgrade that goes far beyond routine version releases. For businesses that rely on scalable and reliable applications, the improvements in Angular 19 are not only helpful but game changing. It transforms how teams build, deploy and maintain applications. This matters because customers today want speed, stability and intuitive interfaces. Angular 19 gives development teams the tools they need to deliver exactly that. Before diving into the new features, it’s important to understand why businesses should care about framework upgrades at all. Older versions often slow down performance, increase maintenance effort and limit the ability to introduce new features quickly. With Angular 19, the framework brings refinements that cut down development effort, improve security and enhance runtime efficiency. When paired with strong engineering practices, these upgrades can turn your digital products into robust assets that scale with your growth. At the heart of Angular 19 is a redefined development experience. The update improves the build system and compiler, making applications load faster and run more smoothly. Businesses competing in crowded markets know that even a one-second improvement in loading time can influence conversions and user satisfaction. The updated rendering pipeline in Angular 19 focuses on speed and reduces overhead, which means your customers interact with your application without lag or disruptions. This alone makes the upgrade worthwhile for teams planning long-term growth. One of the standout improvements is its enhanced reactivity model. Angular 19 simplifies how developers manage state, signals and data flow. In previous versions, reactive patterns could become complex, especially in large enterprise applications. Angular 19 cuts through that complexity with clearer APIs and predictable behavior. For customers, this translates to a more consistent user experience because the interface responds quickly and reliably to every interaction. For businesses, the reduced complexity lowers development time and minimizes the possibility of bugs caused by confusing data flow patterns. Security is another area where Angular 19 moves ahead. Every organization handling customer data, payments or sensitive transactions understands the importance of secure infrastructure. Angular 19 includes updated security defaults, better sanitization and upgraded standards compliance. This strengthens your protection against common vulnerabilities. While security has always been part of the framework, the latest update aligns with modern threats and offers a reliable foundation for growth in regulated industries like finance, healthcare and e-commerce. Another practical advantage is the improved compatibility with modern tooling. Angular 19 pairs more efficiently with TypeScript, modern bundlers and server-side rendering strategies. It supports faster builds, lighter bundles and streamlined testing. Teams upgrading from older versions such as Angular 10 or Angular 12 will immediately notice reduced build times. Faster builds mean quicker development cycles, which helps teams deliver updates, features and fixes without delays. Customers end up with a better product experience because the application evolves without friction. The ecosystem around Angular 19 also brings notable improvements. Updated libraries, better documentation and stronger community support reduce the learning curve for new developers. Companies investing in long-term projects want frameworks that attract both talent and community innovation. Angular 19 makes onboarding simpler, which speeds up hiring and team expansion. For businesses maintaining large codebases, this is a major benefit because it cuts down training time and avoids dependency on a few specialists. From a strategic standpoint, Angular 19 is built to support scalability. It offers improved server-side rendering, partial hydration and better lazy loading options. These features help applications perform well even with heavy traffic or complex logic. Organizations preparing for rapid growth or digital transformation benefit from these capabilities. A smoother load experience keeps customers engaged, especially in high-traffic platforms like marketplaces, portals and service dashboards. The upgrade is also beneficial for companies building multi-platform products. Angular 19 works more seamlessly with mobile and desktop environments, making it easier to maintain a unified codebase. Whether you’re developing customer dashboards, admin systems or client applications, this consistency saves time and reduces ongoing maintenance cost. Customers enjoy a seamless experience across all devices because the framework ensures predictable behavior and consistent performance. For businesses considering long-term support, Angular 19 continues Google’s commitment to stability. The update path is cleaner and designed with enterprise environments in mind. This matters for organizations that cannot afford downtime or risky upgrades. Angular 19 ensures a smoother migration journey compared to older transitions, which often required rewriting entire modules. With this version, the focus is on continuity, reducing the effort needed to keep your product current. If your product roadmap includes AI features, automation workflows or micro-frontend architecture, Angular 19 also provides better integration points. Its updated structure allows smoother communication with APIs, faster rendering of dynamic data and cleaner modular separation. This foundation sets your business up for future expansion without technical barriers that slow you down. For companies aiming to deliver high-quality digital services, using a modern framework is no longer optional. It’s a core requirement for delivering fast, secure and delightful customer experiences. This is why many organizations are moving to Angular Development, as it offers reliability, scalability and a strong ecosystem. And with Angular 19, your development team can build smarter and deliver faster. In conclusion, Angular 19 stands out because it improves performance, simplifies development and strengthens security while staying aligned with enterprise needs. For any organization planning long-term digital growth, adopting Angular Development is a smart investment, and Angular 19 makes the case even stronger by offering a future-ready framework built for modern customer expectations.
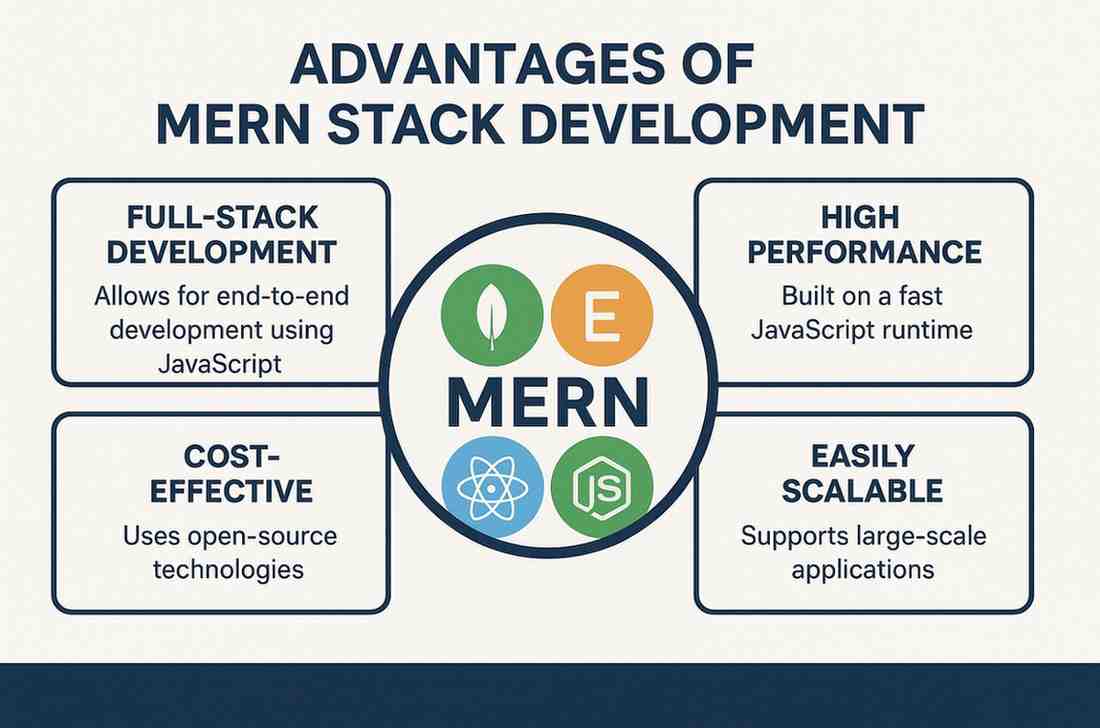
Advantages of MERN Stack Development
Advantages of MERN Stack Development Choosing the right technology stack is one of the most important decisions when building modern web applications. Companies today want faster delivery, scalable architecture and seamless performance across devices. This is where MERN Stack Development stands out as a preferred choice for startups, SMEs and enterprises looking to create powerful digital products. MERN is a JavaScript-based technology stack that includes MongoDB, Express.js, React and Node.js. Together, these technologies create a unified development ecosystem that reduces complexity and increases efficiency. Let’s explore why businesses rely on MERN and how it helps deliver stronger long-term value. 1. End-to-End JavaScript Advantage One of the biggest strengths of MERN is its full JavaScript environment. Both frontend and backend are built using the same language, which simplifies development and makes it easier to onboard teams. Developers don’t need to switch between languages or rewrite logic across layers. This produces faster development cycles, reduced errors and smoother collaboration. In a competitive environment where time-to-market matters, companies benefit from a stack that speeds up every stage of the build. For businesses planning large-scale digital products, MERN Stack Development ensures consistency and efficiency throughout the workflow. 2. Scalability and High Performance Scalability is essential for any growing business. MERN applications scale well, thanks to the architecture of Node.js and MongoDB. Node.js handles a high number of concurrent requests, making it ideal for real-time applications such as chat apps, dashboards and streaming platforms. Meanwhile, MongoDB’s document-based structure allows flexible and fast data storage that can grow as your business evolves. This combination supports applications that need to serve thousands or even millions of users without performance issues. When companies expect long-term customer growth, choosing a stack built for scale becomes a strategic advantage. 3. React Enables Superior User Experiences Customer experience is at the heart of every successful digital product. React, the frontend library in MERN, offers a component-based structure that helps developers build interactive, responsive and user-friendly interfaces. Performance optimization features like virtual DOM ensure pages load quickly, even with dynamic content. Businesses benefit directly through higher engagement, better conversion rates and improved satisfaction. Whether it’s a customer portal, booking system or e-commerce storefront, React makes it easier to deliver polished experiences that feel modern and intuitive. 4. Faster Development Through Reusable Components MERN encourages modular development. Components created in React, routes built in Express.js and schemas designed in MongoDB can be reused across different parts of the application. This reduces development effort and helps teams maintain a consistent structure. For companies managing complex products or multiple platforms, this is a major cost-saving factor. Reusability also improves maintainability, making it easier to update or scale the application without rebuilding everything from scratch. 5. Strong Ecosystem and Community Support MERN has a large and active global community. This means developers have access to tutorials, tools, libraries and ready-made solutions. For businesses, this leads to faster troubleshooting, more innovation and lower engineering risks. Community-driven technologies evolve quickly, which ensures the product remains future-ready. Companies can integrate new features, adopt best practices and stay aligned with industry standards without heavy overhead. 6. Cost-Effective for Startups and Enterprises Since MERN uses open-source technologies, businesses save significantly on licensing fees. Development is also more efficient because the entire stack relies on one language and a well-integrated architecture. This reduces the need for large teams with varied technical backgrounds. Startups appreciate MERN because it offers speed, flexibility and affordability. Enterprises appreciate it for scalability and long-term maintainability. The cost-to-value ratio is one of the highest among modern full-stack development options. 7. Easy Integration With Cloud Services Modern applications often depend on cloud platforms for hosting, databases, analytics, authentication and file storage. MERN integrates smoothly with AWS, Google Cloud, Azure and other major providers. Node.js in particular offers a wide range of SDKs and APIs that simplify cloud adoption. This helps businesses reduce infrastructure complexity and focus more on the actual product. Deployments become smoother, upgrades are easier and long-term operational costs stay under control. 8. Ideal for Building Single-Page and Enterprise Apps MERN is well suited for businesses looking to build single-page applications (SPAs), enterprise dashboards, CRM systems, custom portals and SaaS platforms. React’s fast rendering and Node.js’s real-time capabilities make the stack perfect for high-performance applications. Companies that want flexibility, speed and a modern interface often find MERN to be the ideal match.
Possible Vulnerabilities of Using WordPress for Your Business Websites
Possible Vulnerabilities of Using WordPress for Your Business Websites WordPress powers a large share of business websites today. It is flexible, easy to deploy and supported by a huge ecosystem of plugins and themes. But the same strengths that make WordPress popular also introduce security risks that growing companies cannot ignore. If your business depends on a stable online presence, it’s important to understand where vulnerabilities come from and how to manage them effectively. Many of these risks can be reduced with Customized WordPress Development, but they still deserve close attention. 1. The Open-Source Nature of WordPress WordPress is open source. This means the code is freely available, well documented and constantly reviewed by developers. It also means attackers have access to the same code and can look for weaknesses. When a vulnerability becomes public, bots and malicious actors quickly scan the internet for websites that haven’t patched it. Businesses often delay updates because they worry about breaking something on a live site. That delay creates a window for attacks. A professional team using Customized WordPress Development can help ensure updates are tested and deployed safely, which reduces exposure without harming performance. 2. Excessive Use of Plugins Plugins make WordPress powerful, but they’re also one of the most common attack points. A typical business website uses 15 to 40 plugins. Each one adds a new layer of code that can carry bugs, outdated functions or hidden security flaws. Some plugin developers abandon their projects, leaving known vulnerabilities unfixed. Others may not follow secure coding standards. Attackers target popular plugins because compromising one plugin can expose millions of websites. Businesses that install plugins without checking the developer reputation or support cycle put their websites at risk. A curated and optimized setup developed through Customized WordPress Development helps reduce plugin dependency and ensures that only high-quality, secure plugins remain part of your system. 3. Vulnerable Themes and Templates Themes shape the look and feel of a WordPress site. Many free and low-cost themes are poorly coded. They include outdated libraries, insecure JavaScript, or unnecessary features that increase the attack surface. Some themes come bundled with plugins you may never use, but they still run in the background and create vulnerabilities. Premium themes can also be problematic if they are purchased once and never updated. When businesses modify themes manually, they sometimes break update compatibility, which forces them to postpone necessary security patches. Custom theme development or child-theme implementation by a skilled team is the best way to keep branding unique without sacrificing security. 4. Weak Authentication Practices WordPress login pages are a popular target for brute-force attacks. Automated scripts try thousands of username-password combinations to gain entry. If your users rely on weak passwords, admin accounts can be compromised quickly. Other issues include: Default login URLs Lack of multi-factor authentication Shared or reused admin credentials Unrestricted login attempts These may sound basic, but many breaches trace back to simple authentication mistakes. Businesses should enforce strong password policies, hide default login paths and use MFA. Tools and custom workflows can help, especially when managed by a dedicated development team. 5. Outdated Core Installations WordPress releases frequent updates that include security improvements. When companies delay installing these updates, vulnerabilities accumulate. Sites running older versions of PHP face even bigger risks because outdated PHP versions no longer receive security fixes. Small businesses often rely on shared hosting environments where updating PHP or server modules isn’t immediately possible. Without timely updates, even minor threats can escalate into major breaches. Using staging environments and automated update testing helps reduce the risk of breaking your site while staying secure. 6. Exposure Through Shared Hosting To save costs, many businesses host their WordPress sites on shared servers. While this keeps expenses low, it introduces security challenges. If one website on the shared server is compromised, attackers may gain access to other sites hosted on the same machine. Shared hosting also limits control over file permissions, server configurations and firewall settings. Higher-tier hosting or managed WordPress hosting significantly reduces vulnerability and gives businesses the security transparency they need. 7. Lack of Regular Security Audits WordPress installations change over time. New pages, plugins, user accounts and integrations all affect security. But many companies build a site once and rarely conduct audits. This creates blind spots. Files may be infected without noticeable symptoms, or malicious scripts may lie dormant. Security audits help uncover: File system changes Suspicious login activity Outdated plugins or themes Malware injections Database anomalies Routine security audits and monitoring tools allow businesses to detect issues early instead of reacting when damage is already done. 8. Human Errors and Poor Maintenance Not all vulnerabilities come from software. Human mistakes remain one of the biggest risks. Examples include: Granting admin access to users who don’t need it Installing plugins from unverified sources Ignoring backup practices Uploading infected files Training, documentation and structured workflows help reduce these errors. A proper development and maintenance approach keeps your website protected long term. Conclusion WordPress is a strong platform for business websites, but it needs disciplined management to stay secure. Most vulnerabilities come from outdated components, poor maintenance routines and unmanaged plugin ecosystems. With the right processes, hosting environment and regular audits, you can use WordPress safely and reliably. Investing in Customized WordPress Development ensures your site is optimized, secured and tailored for long-term growth.